GSoC: External Workspace Manager for Pipeline. Beta release is available
This blog post is a continuation of the External Workspace Manager Plugin related posts, starting with the introductory blog post, and followed by the alpha version release announcement.
As the title suggests, the beta version of the External Workspace Manager Plugin was launched! This means that it’s available only in the Experimental Plugins Update Center.
| Take care when installing plugins from the Experimental Update Center, since they may change in backward-incompatible ways. It’s advisable not to use it for Jenkins production environments. |
What’s new
Bellow is a summary of the features added so far, since the alpha version.
Multiple upstream run selection strategies
It has support for the Run Selector Plugin (which is still in beta), so you can provide different run selection strategies when allocating a disk from the upstream job.
Let’s suppose that we have an upstream job that clones the repository and builds the project:
def extWorkspace = exwsAllocate 'diskpool1'
node ('linux') {
exws (extWorkspace) {
checkout scm
sh 'mvn clean install -DskipTests'
}
}In the downstream job, we run the tests on a different node, but we reuse the same workspace as the previous job:
def run = selectRun 'upstream'
def extWorkspace = exwsAllocate selectedRun: run
node ('test') {
exws (extWorkspace) {
sh 'mvn test'
}
}The selectRun in this example selects the last stable build from the upstream job.
But, we can be more explicit, and select a specific build number from the upstream job.
def run = selectRun 'upstream',
selector: [$class: 'SpecificRunSelector', buildNumber: UPSTREAM_BUILD_NUMBER]
def extWorkspace = exwsAllocate selectedRun: run
// ...When the selectedRun parameter is given to the exwsAllocate step, it will allocate the same workspace that was
used by that run.
The Run Selector Plugin has several run selection strategies that are briefly explained here.
Automatic workspace cleanup
Provides an automatic workspace cleanup by integrating the Workspace Cleanup Plugin. For example, if we need to delete the workspace only if the build has failed, we can do the following:
def extWorkspace = exwsAllocate diskPoolId: 'diskpool1'
node ('linux') {
exws (extWorkspace) {
try {
checkout scm
sh 'mvn clean install'
} catch (e) {
currentBuild.result = 'FAILURE'
throw e
} finally {
step ([$class: 'WsCleanup', cleanWhenFailure: false])
}
}
}More workspace cleanup examples can be found at this link.
Custom workspace path
Allows the user to specify a custom workspace path to be used when allocating workspace on the disk. The plugin offers two alternatives for doing this:
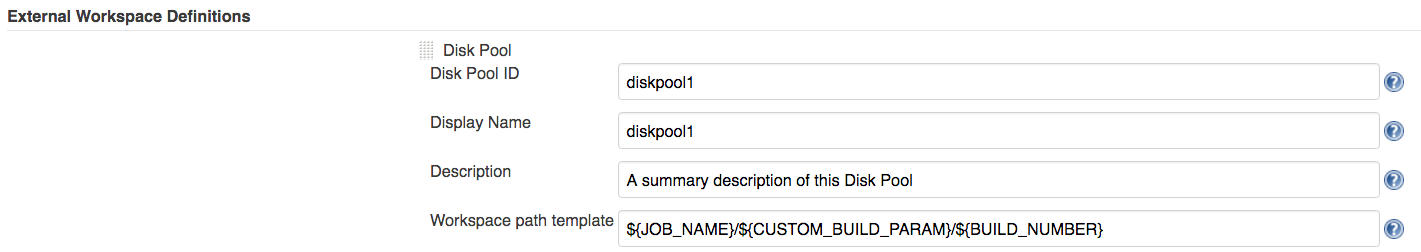
-
by defining a global workspace template for each Disk Pool
This can be defined in the Jenkins global config, External Workspace Definitions section.
-
by defining a custom workspace path in the Pipeline script
We can use the Pipeline DSL to compute the workspace path.
Then we pass this path as input parameter to the exwsAllocate step.
def customPath = "${env.JOB_NAME}/${PULL_REQUEST_NUMBER}/${env.BUILD_NUMBER}"
def extWorkspace = exwsAllocate diskPoolId: 'diskpool1', path: customPath
// ...For more details see the afferent documentation page.
Disk Pool restrictions
The plugin comes with Disk Pool restriction strategies. It does this by using the restriction capabilities provided by the Job Restrictions Plugin.
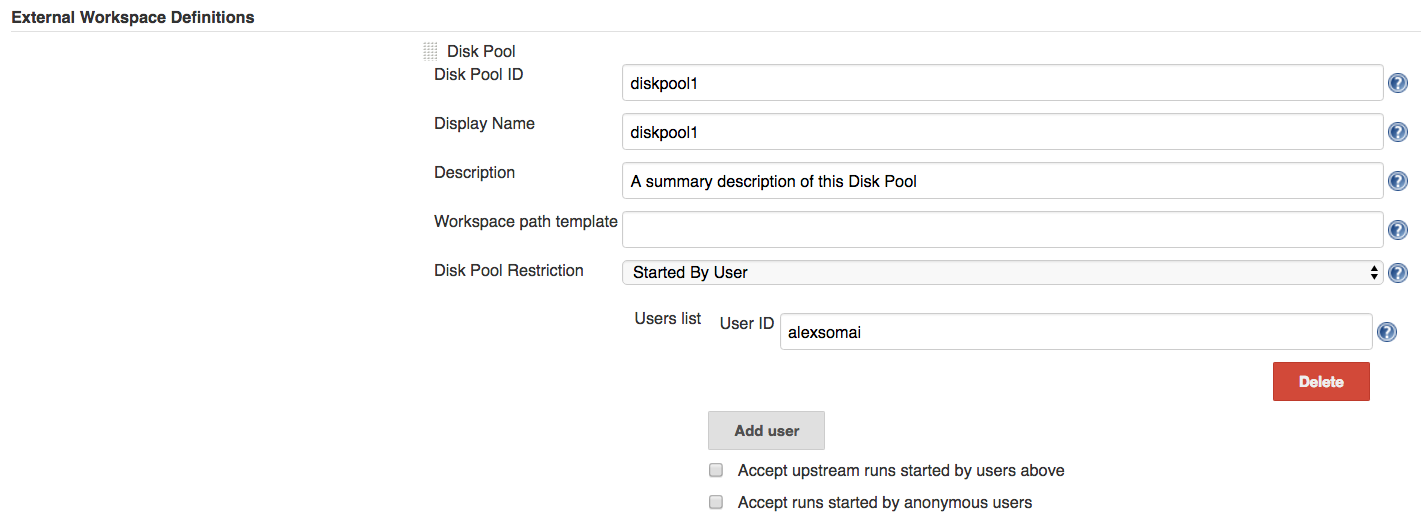
For example, we can restrict a Disk Pool to be allocated only if the Jenkins job in which it’s allocated was triggered by a specific user:
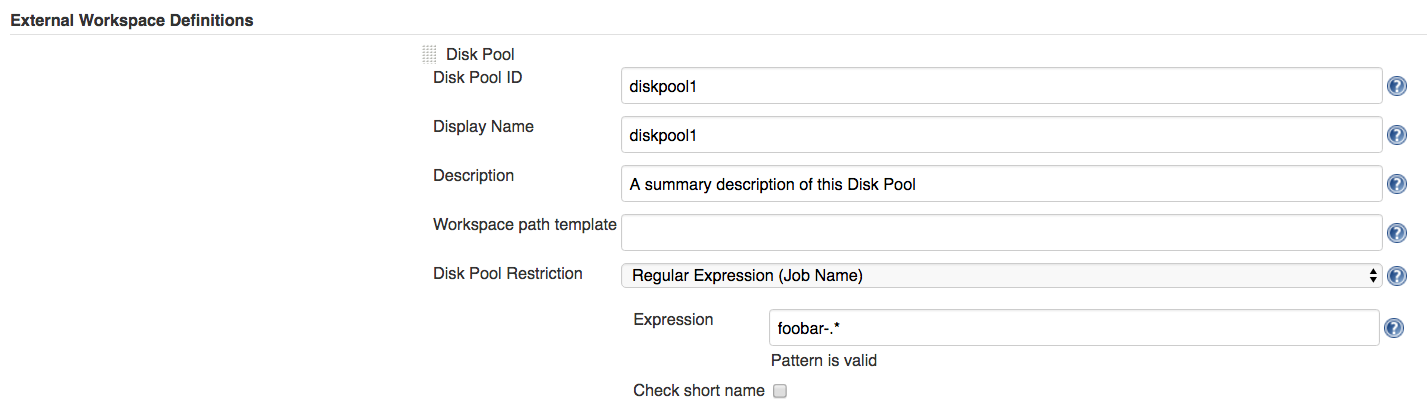
Or, we can restrict the Disk Pool to be allocated only for those jobs whose name matches a well defined pattern:
What’s next
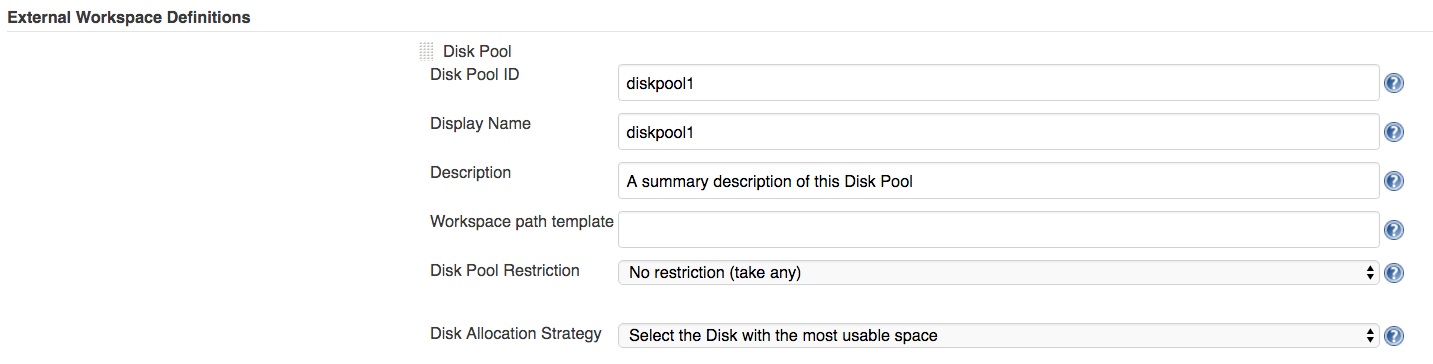
Currently there is ongoing work for providing flexible disk allocation strategies. The user will be able to define a default disk allocation strategy in the Jenkins global config. So for example, we want to select the disk with the most usable space as default allocation strategy:
If needed, this allocation strategy may be overridden in the Pipeline code. Let’s suppose that for a specific job, we want to allocate the disk with the highest read speed.
def extWorkspace = exwsAllocate diskPoolId: 'diskpool1', strategy: fastestRead()
// ...When this feature is completed, the plugin will enter a final testing phase. If all goes to plan, a stable version should be released in about two weeks.